
Overview
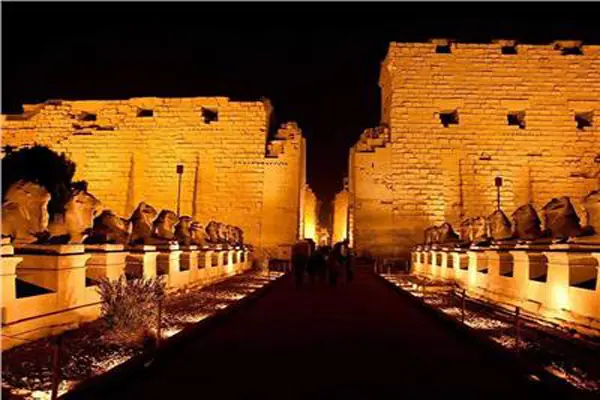
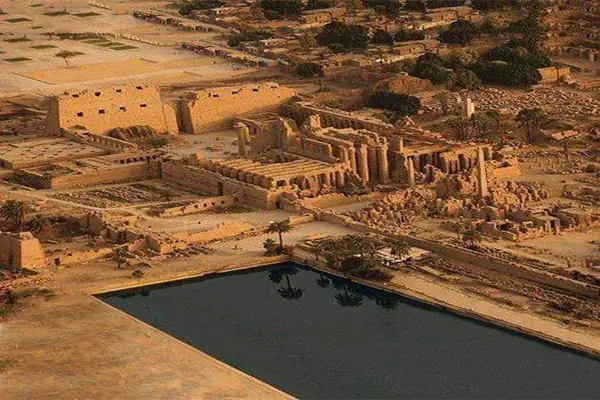
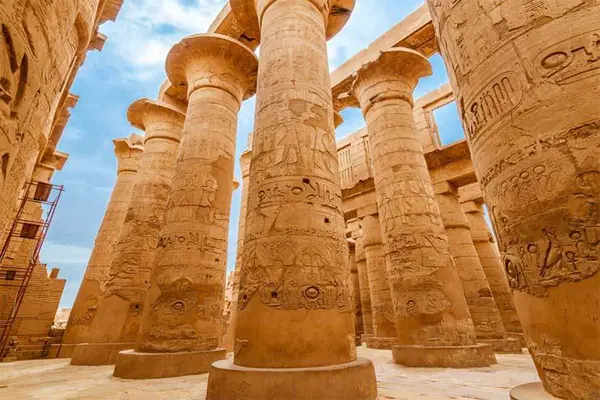
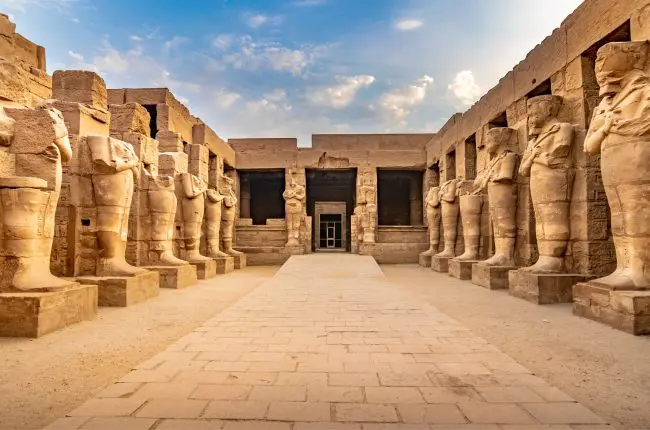
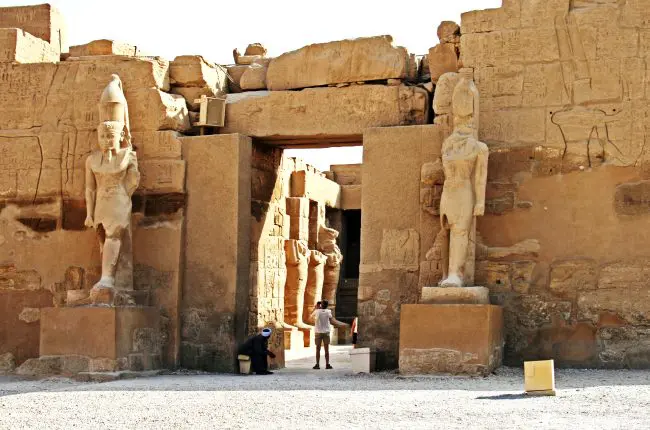
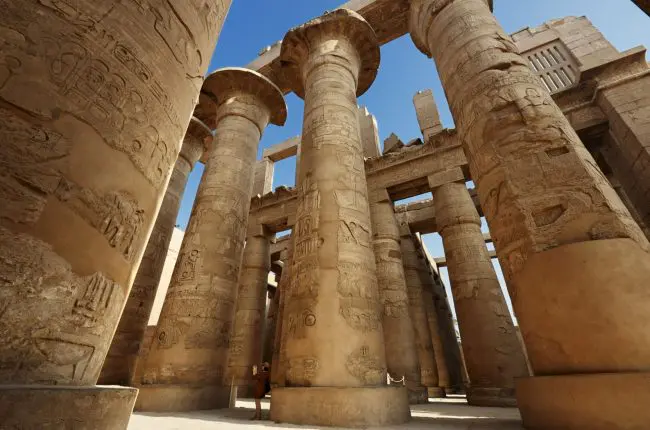
Karnak Temple is a huge complex of temples and religious buildings located in Luxor, Egypt. It was built on the occasion of the god of war, Amun-Ra, and was used as a religious and administrative center during the New Kingdom of Egypt. The temple was built in different stages and includes many embankments, chapels and courtyards. The main hall of the temple is distinguished by the Great Temple of Amun, which includes a row of columns more than 14 meters high and a courtyard surrounded by walls with a length of 100 meters. Karnak Temple is one of the largest and most beautiful ancient sites in the world and an architectural masterpiece of ancient Egypt.Sights
Map
Info
Date of Establishment of the Temple: The Karnak Temple was built in different stages over a period of more than 1,500 years, from the Middle Kingdom to the Ptolemaic period in the history of Egypt. The religious complex was dedicated to the god Amun-Ra, and was used as a religious and administrative center during the New Empire in Egypt. The original complex began as a small temple dedicated to the god Amun and was built by Pharaoh Senusret I in the 13th century BC. Over time, other pharaohs expanded and improved it, including Thutmose I, Hatshepsut, and Ramesses II. During the reign of Amenhotep IV (Akhenaten), construction of a temple began in the city of Akhetaten (now Amarna) in honor of the god Aten. After his death, however, his successor Tut abandoned the project and restored the traditional worship of Amun at Karnak. After that, the Karnak Temple fell into disuse and was abandoned during the Ptolemaic period. In the first century BC, the Roman Egyptians moved the temple and are known to have repaired it and built some new structures. In short, the history of Karnak Temple is long and complex, and it has many stages of construction and changes in its function and worship over the centuries.














