
Overview
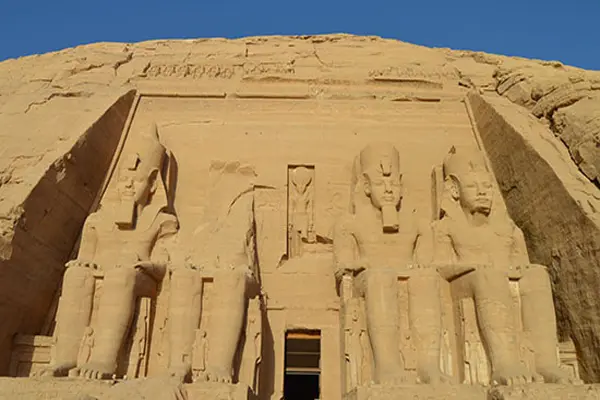
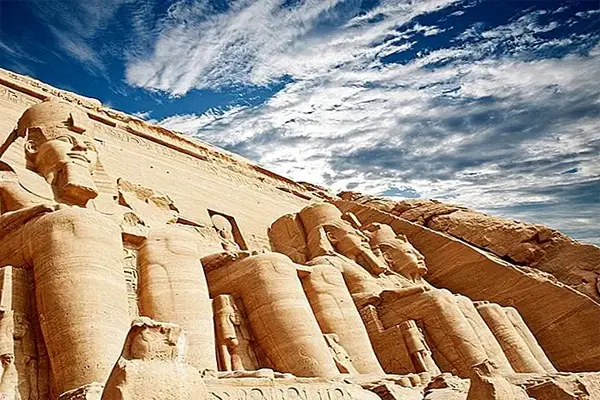
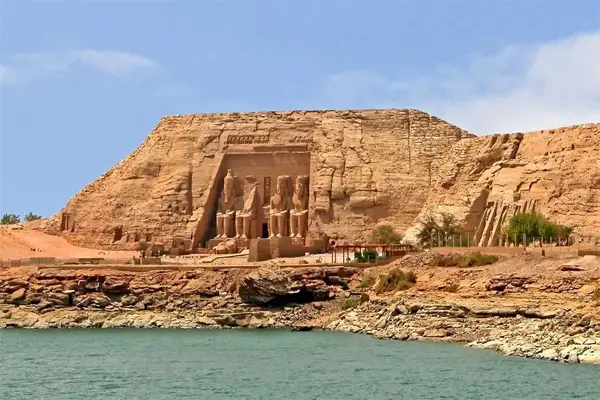
Abu Simbel Temple is one of the famous ancient temples in Egypt and is located in the south of the city of Aswan. The ruins in the temple are among the most important historical monuments in Egypt and show the highness and military power that King Ramesses II enjoyed. The Abu Simbel Temple was designed during the reign of King Ramesses II in the thirteenth century BC, and was built as a tomb for the same king as well as for the god Amun-Ra. The temple is considered one of the giant temples of the Pharaonic era, reaching a height of more than 30 meters.Map
Info
The Abu Simbel Temple is famous for the huge statues located in front of the main entrance to the temple, as it is represented by statues of King Ramses II, the statue of his wife Nefertari, and the statue of the sun god Ra. The Abu Simbel Temple is one of the most visited tourist sites in Egypt, where thousands of tourists are hosted every year to see these wonderful monuments. The history of the Abu Simbel Temple dates back to the Pharaonic era, specifically to the reign of King Ramesses II in the thirteenth century BC. It is believed that the temple was originally used as a mortuary temple for King Ramesses II and his wife, Nefertari. In the year 1960, the Egyptian government expanded the High Dam Lake, which was built on the Nile River in southern Egypt, and this posed a threat to the temple located in the region. The Egyptian government, in cooperation with the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO), decided to move the temple to a safe location. The temple was moved from its original location to a new location about 210 meters to the east and 60 meters to the north, and this was done by means of a huge international project that lasted for six years, as the temple was dismantled and shipped in parts to its new location, and the temple was rebuilt and restored in a style that simulates the original site. In the year 1980 AD, the Abu Simbel Temple was included in the UNESCO World Heritage Sites.











